Home › Kettlebell Training › Kettlebell Guide
If you’re new to kettlebell training, read the complete kettlebell training guide before starting workouts.
 Kettlebell training is one of the most effective ways to build strength, improve endurance, and enhance overall fitness. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced lifter, proper technique is essential to maximize results and prevent injuries. Unlike traditional weights, kettlebells challenge your stability, coordination, and grip strength, making them a versatile tool for full-body workouts. This guide will cover essential kettlebell training tips to help you refine your form, avoid common mistakes, and get the most out of every session.
Kettlebell training is one of the most effective ways to build strength, improve endurance, and enhance overall fitness. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced lifter, proper technique is essential to maximize results and prevent injuries. Unlike traditional weights, kettlebells challenge your stability, coordination, and grip strength, making them a versatile tool for full-body workouts. This guide will cover essential kettlebell training tips to help you refine your form, avoid common mistakes, and get the most out of every session.
The Significance of Kettlebell Training in Strength and Conditioning
Kettlebell workouts have surged in popularity due to their ability to enhance functional strength, endurance, and mobility in ways that conventional training methods often overlook. Unlike traditional dumbbells or barbells, kettlebells have a displaced center of gravity, requiring increased stabilization, coordination, and neuromuscular engagement. This unique design challenges multiple muscle groups simultaneously, fostering superior movement efficiency and athleticism.
Why Kettlebells Are a Game-Changer
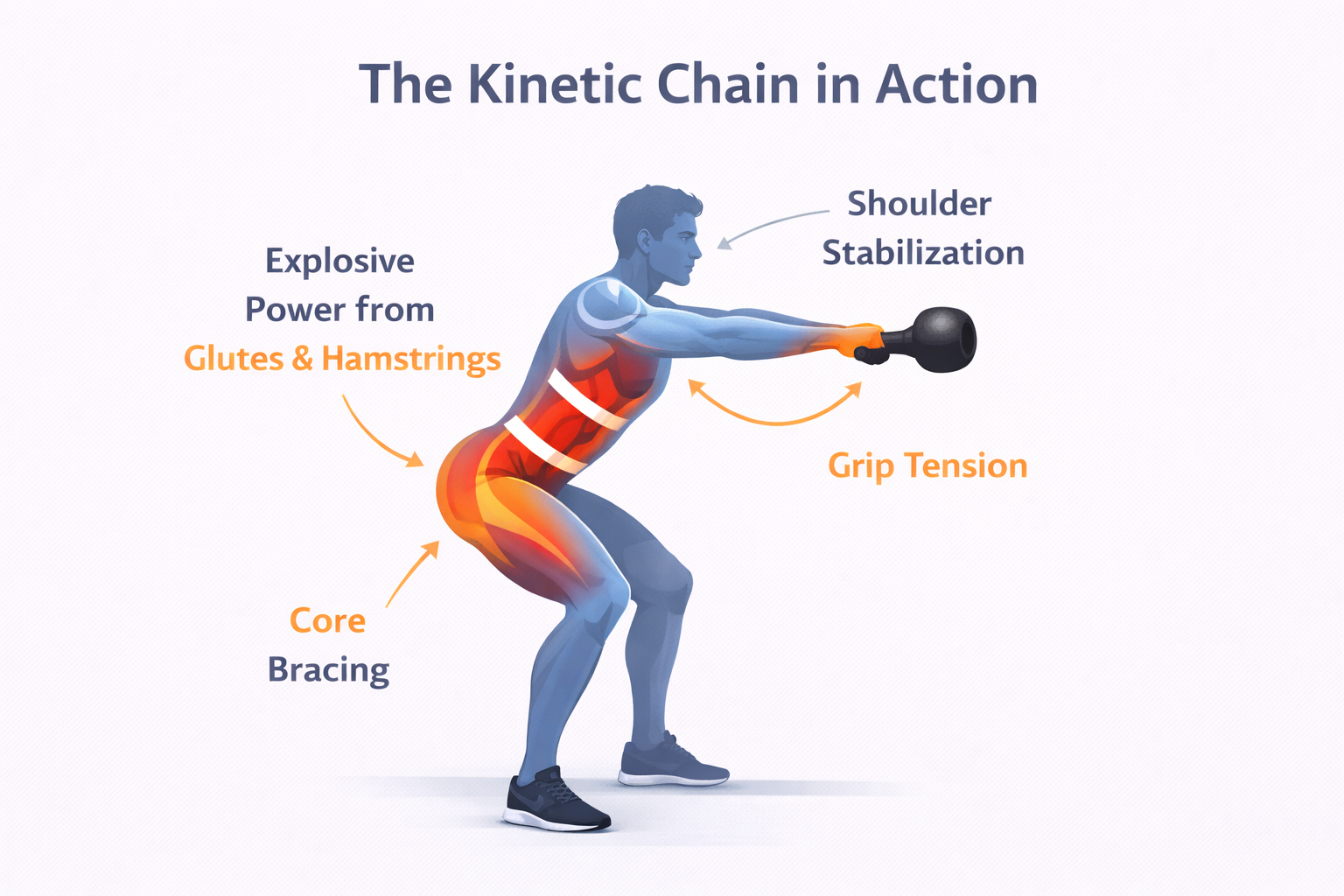
Kettlebell drills are not just about lifting weight—they promote a seamless blend of power, stability, and endurance. Below are key reasons why incorporating them into your regimen can revolutionize your fitness approach:
- Enhanced Kinetic Chain Activation – Kettlebell movements engage multiple muscle groups in synchrony, reinforcing full-body coordination and core stability. Unlike isolated exercises, they mimic real-world motions, improving strength transfer to daily activities and sports performance.
- Metabolic Amplification – Due to the dynamic nature of kettlebell drills, they elevate heart rate rapidly, making them an excellent tool for metabolic conditioning. The combination of resistance and cardio-driven movement accelerates caloric expenditure, optimizing fat oxidation and endurance.
- Grip and Forearm Fortification – The thick handles of kettlebells demand greater grip endurance, enhancing forearm strength over time. This not only improves performance in lifting disciplines but also benefits activities that require a powerful grip, such as rock climbing and martial arts.
- Postural and Mobility Enhancement – Traditional resistance training often neglects postural alignment and mobility. Kettlebell training integrates dynamic movement patterns that reinforce proper spinal positioning, joint mobility, and flexibility. This reduces injury risk and enhances movement mechanics.
- Time-Efficient Training – A well-structured kettlebell workout eliminates the need for excessive equipment, allowing for high-intensity training in minimal time. Whether for strength-building, endurance, or fat loss, kettlebells deliver maximum results with fewer sets and repetitions.
Building a Stronger, More Resilient Body
Kettlebell training is more than just an alternative to free weights—it is a transformative method that builds functional strength, conditions the cardiovascular system, and refines movement efficiency. Whether incorporated into a structured strength program or used for standalone conditioning, kettlebells provide an unparalleled blend of power and agility. By mastering their mechanics and applying the right techniques, you can unlock untapped potential and elevate your performance to new heights.
Mastering Kettlebell Movements: Essential Techniques for Efficiency
Executing kettlebell exercises with precision is crucial for maximizing strength gains while preventing strain or injury. Unlike standard free weights, kettlebells demand controlled movement patterns, requiring balance, coordination, and proper engagement of stabilizing muscles. Below is a breakdown of fundamental kettlebell movements and their key benefits.
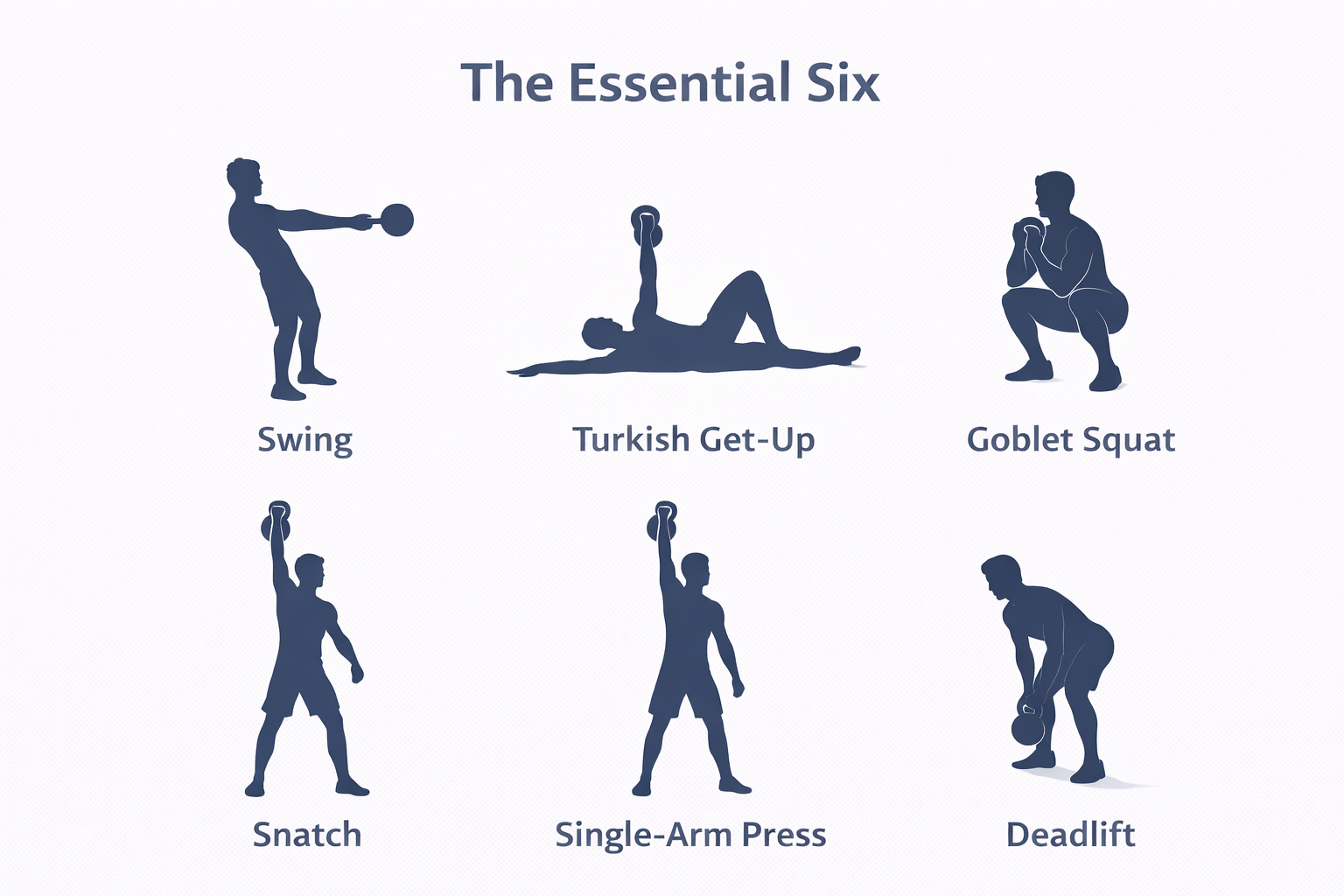
Essential Kettlebell Movements and Their Benefits
| Exercise | Primary Muscles Engaged | Key Benefits |
| Kettlebell Swing | Glutes, Hamstrings, Core | Explosive power, hip hinge mastery, cardio endurance |
| Turkish Get-Up | Shoulders, Core, Hips | Full-body control, stability, injury prevention |
| Goblet Squat | Quadriceps, Core, Glutes | Lower body strength, mobility, posture improvement |
| Kettlebell Snatch | Shoulders, Back, Core | Power development, coordination, metabolic boost |
| Single-Arm Press | Deltoids, Triceps, Core | Upper body strength, unilateral stability |
| Kettlebell Deadlift | Hamstrings, Glutes, Core | Posterior chain activation, grip fortification |
Mastering these fundamental exercises creates a strong foundation for more complex movements. Proper execution not only amplifies muscle activation but also optimizes efficiency, ensuring every repetition contributes to performance gains.
Elevating Your Kettlebell Workouts: Maximizing Effectiveness
To ensure kettlebell training delivers optimal results, consider fine-tuning your approach by implementing key strategies that enhance strength, endurance, and overall progression.
Techniques to Enhance Performance

- Refine Your Grip Mechanics – Kettlebell handles require a firm yet adaptable grip. Avoid over-gripping, as excessive tension can lead to early fatigue. Instead, maintain a relaxed but controlled hold, particularly during ballistic movements like swings and cleans.
- Engage the Posterior Chain – Many kettlebell movements, such as deadlifts and swings, rely on the posterior chain—hamstrings, glutes, and lower back. Proper engagement ensures efficient force generation while reducing strain on the lower back.
- Breathe with Intention – Controlled breathing plays a vital role in maintaining stability and endurance. Exhale during exertion phases, such as the upward movement of a snatch or press, to maximize force output.
- Utilize Unilateral Training – Single-arm movements improve muscular imbalances and reinforce core activation. Incorporate unilateral exercises like single-arm swings and presses to develop balanced strength.
- Optimize Time Under Tension – Slower, controlled repetitions increase muscle engagement. For strength-building, focus on a steady eccentric phase, allowing muscles to absorb tension and build resilience.
By integrating these techniques into your kettlebell regimen, you refine your execution, ensuring each session contributes to sustained progress and efficiency.
Fundamental Kettlebell Training Tip: Master the Hip Hinge
One of the most overlooked yet essential techniques in kettlebell training is the hip hinge—a movement pattern critical for generating power, preventing injury, and executing exercises effectively. Many beginners mistakenly squat during movements that require hinging, limiting force production and increasing strain on the lower back.
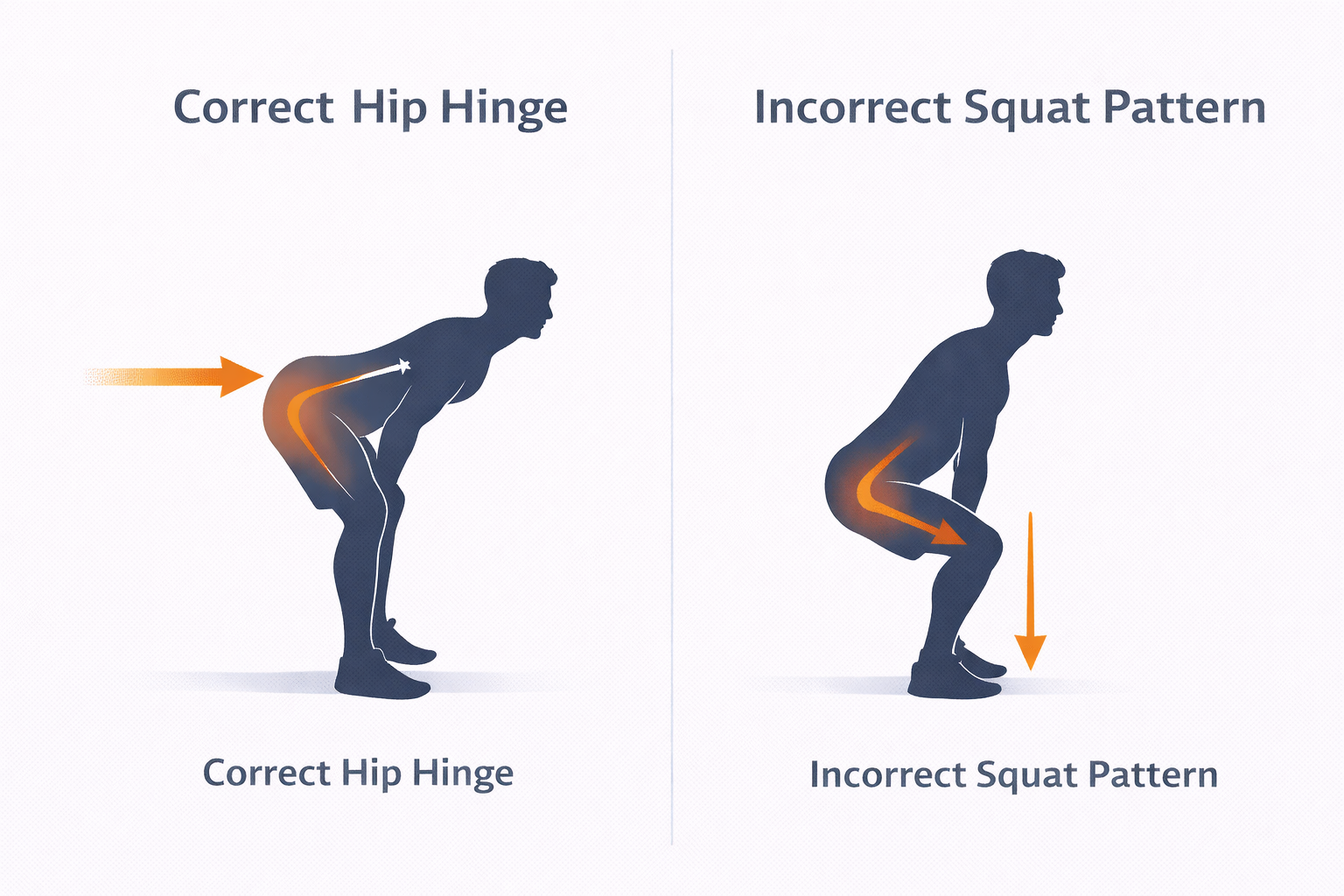
How to Perfect Your Hip Hinge
- Set Your Stance – Stand with feet hip-width apart, ensuring a firm and balanced base. Keep your weight distributed evenly across your feet.
- Brace Your Core – Engage your abdominals to stabilize the spine, preventing excessive arching or rounding of the back.
- Hinge at the Hips – Push your hips backward while maintaining a slight bend in the knees. The goal is to create a stretch in the hamstrings without excessive knee flexion.
- Keep the Back Neutral – Avoid rounding or overarching. Maintain a straight spine from the neck to the lower back.
- Drive Through the Hips – At the top of the movement, squeeze your glutes and extend your hips fully without leaning backward.
The hip hinge is foundational for kettlebell swings, deadlifts, and cleans. Mastering this technique improves performance while reducing unnecessary stress on the lower back, ensuring longevity in training.
Frequently Asked Questions About Kettlebell Training
What are the best kettlebell exercises for strength development?
Kettlebell deadlifts, presses, and Turkish get-ups are highly effective for building strength by engaging multiple muscle groups and reinforcing stability.
How heavy should my kettlebell be as a beginner?
For beginners, men can start with 12-16kg (26-35 lbs.) and women with 8-12kg (18-26 lbs.). Prioritize proper technique before progressing to heavier weights.
How often should I do kettlebell training for optimal results?
For strength and endurance, 3-4 sessions per week provide adequate stimulus while allowing recovery. Adjust frequency based on intensity and training goals.
Is kettlebell training good for fat loss?
Yes, high-intensity kettlebell exercises like swings and snatches elevate heart rate, promoting calorie burn and fat loss when combined with proper nutrition.
Can kettlebell workouts replace traditional weightlifting?
Kettlebell training enhances functional strength and endurance but can complement rather than replace barbell training, depending on your goals.
Final Thoughts on Kettlebell Training for Strength and Endurance
Kettlebell training is a versatile and efficient approach to developing full-body strength, enhancing endurance, and improving movement mechanics.

Its dynamic nature engages multiple muscle groups, promotes cardiovascular conditioning, and strengthens grip endurance. By focusing on proper technique, incorporating progressive overload, and refining movement patterns, you can maximize the benefits of every session. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced athlete, kettlebells offer a scalable and effective training method that fosters long-term strength and resilience.
